Eruption of the first tooth in your child’s mouth is the one of the most awaited time for a parent. Most of the parents are aware that the first tooth of the child starts erupting at the age of 6 months. But sometimes there can be a delay in teething and you need not worry much about it. You can wait till the age of 15 months to 18 months for the first tooth to erupt in your child’s mouth.
Here is the tooth eruption chart you can co-ordinate with and check the eruption progress in your child’s mouth.
All the 20 teeth should erupt in the child’s mouth by the age of 3 years.
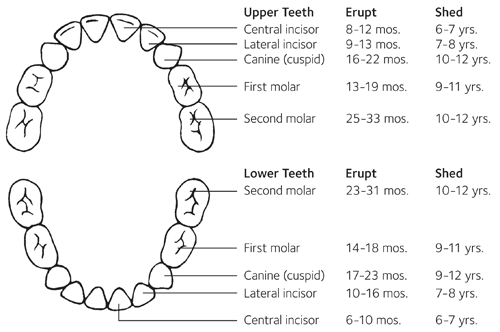
Source: American Dental Association
| Tooth | Age of Eruption |
| Lower Central Incisor | 6-10 Months |
| Lower Lateral Incisor | 10-16 Months |
| Lower Canine | 17-23 Months |
| Lower First Molar | 14-18 Months |
| Lower Second Molar | 23-31 Months |
| Upper Central Incisor | 8-12 Months |
| Upper Lateral Incisor | 9-13 Months |
| Upper Canine | 16-22 Months |
| Upper First Molar | 13-19 Months |
| Upper Second Molar | 25-33 Months |
Related: Baby Developmental Milestones 0-12 Months
Natal Teeth
Some kids are born with teeth in their mouth. These are known as the natal teeth. Often the natal teeth are the mandibular central incisors i.e. the front lower teeth. If your child has the natal teeth and you get them extracted right after birth your child will not have those milk teeth again. These teeth will only be replaced by the permanent teeth between the age of 6-7 years.
Neonatal Teeth
Neonatal teeth are different from the natal teeth. Neonatal teeth are the teeth that erupt within the first month of life. These are also most of the times the lower central incisors.
The eruption sequence and time of teeth can vary from one baby to the other. Never compare two kids. If in doubt visit your dentist preferably a pedodontist and get it checked. Your dentist is the best judge.
Related: At what age should my child see an Orthodontist?
Disclaimer:
This blog provides general information about tooth eruption chart for milk teeth. The opinion and content on this blog is only for conversational purposes and should not be interpreted as medical or dental advice pertaining to any particular individual. If the reader or any other person has a medical or dental concern, he or she should consult with an appropriate licensed medical or dental physician or a health care provider.





Pingback: Natal and Neonatal Teeth - DentistMaa
Useful information
Thank you so much 🙂 Hope it helped 🙂